ADVERTISEMENT

HydroWiz Pipe Flow Hydraulics
Tools
4.6
100+
Revisión del editor
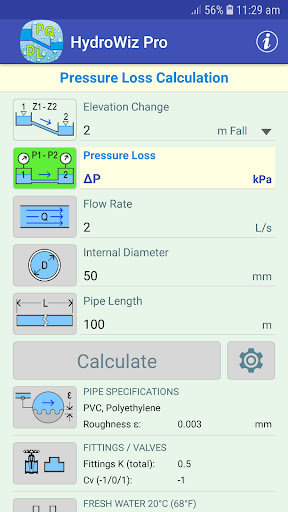
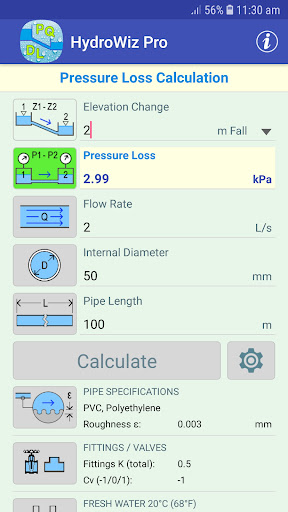
HydroWiz was designed to be a versatile tool to help engineers with their pipe flow hydraulic calculations allowing them to perform quick "what if?" calculations easily. It would also be useful to anyone working on simple water transfer projects involving pipes. The app solves the Darcy-Weisbach equation, the Colebrook-White equation and Bernoulli's equation to perform a range of hydraulic calculations on a single length of pipe between two known points.
MAIN CALCULATIONS
• P1 Pressure - calculates the pressure at the start of the line at P1.
• P2 Pressure - calculates the pressure at the end of the line at P2.
• Q Flow Rate - calculates the volumetric flow rate in the pipe.
• D Internal Diameter - calculates the internal diameter of the pipe.
• L Pipe Length - calculates the pipe length between P1 and P2.
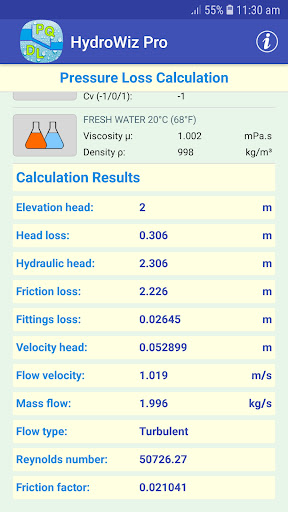
OTHER CALCULATION RESULTS
• Pressure loss.
• Head loss.
• Elevation head.
• Hydraulic head.
• Friction loss.
• Fittings loss.
• Velocity head.
• Flow velocity.
• Mass flow.
• Flow type.
• Reynolds number.
• Friction factor.
INPUT REQUIREMENTS
• P1 Pressure - elevation change, P2 pressure, flow rate, internal diameter and pipe length.
• P2 Pressure - elevation change, P1 pressure, flow rate, internal diameter and pipe length.
• Q Flow Rate - elevation change, P1/P2 pressure, internal diameter and pipe length.
• D Internal Diameter - elevation change, P1/P2 pressure, flow rate and pipe length.
• L Pipe Length - elevation change, P1/P2 pressure, flow rate and internal diameter.
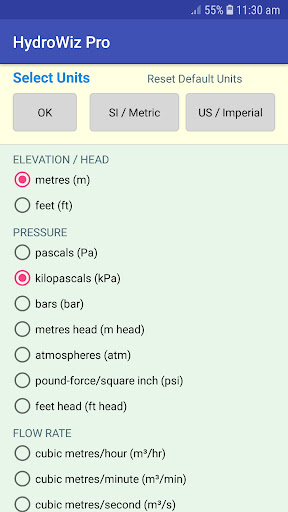
SYSTEM AND UNIT OPTIONS
• Preferred units of measurement in both SI/Metric and US/Imperial units.
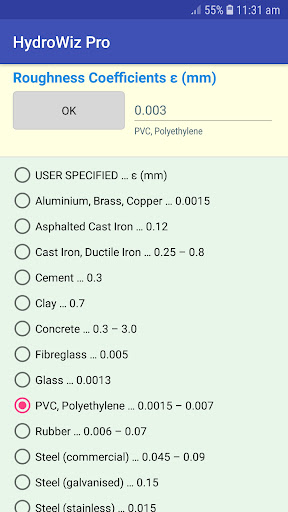
• Pipe roughness coefficients from a range of pipe materials.
• Resistance coefficients from commonly used pipe fittings and valves.
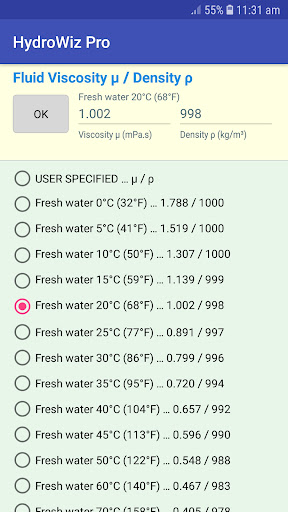
• Fluid properties from a range of fluids including fresh water and sea water at different temperatures.
NOTE ON CRITICAL FLOW ZONE (2300 < Re < 4000)
It is well recognized that the flow within this narrow zone is unpredictable, unstable and not fully understood. The best practice is to design within the laminar flow or turbulent flow zones to avoid potential problems and uncertainty. Any calculation falling inside this zone will be issued with a warning. The calculated results are average values but can vary significantly due to both friction factor and flow instability.
ADVERTISEMENT